What is Keratoconus?
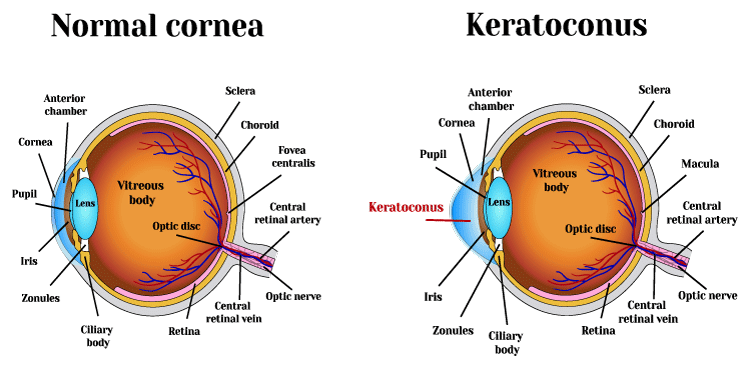
Keratoconus is a degenerative disease of the cornea or the thin lens through which we see. Over time, the cornea thins and steepens. Instead of maintaining its dome-like shape, the cornea bulges out in a cone shape that can greatly distort vision and lead to permanent eye damage.
How Prevalent is Keratoconus? And are Certain People at Greater Risk?
It is estimated that this disease affects 1 in 2000 individuals. The diagnosis often happens in the teenage years.
How do I Know if I Might Have Keratoconus?
Individuals with keratoconus often notice vision distortions before changes in sight. Symptoms might include: ghosting, seeing multiples, halos, blurred vision, and starbursts around lights.
What are My Options for Correcting Poor Vision if I have Keratoconus?
A keratoconus lens specialist can help fit an individual with contact lenses that will fit their unique situation. If soft contact lenses are not appropriate, rigid gas permeable (RGP) contacts may be recommended. If the condition is severe enough, a corneal transplant may be the preferred course of treatment.
Corneal Ectasia or Secondary Keratoconus
Corneal Ectasia is sometimes referred to as secondary keratoconus. It is most often associated with LASIK procedures. LASIK permanently thins and weakens the cornea. If a patient does not have keratoconus prior to LASIK surgery, and steepening and vision loss is detected post-surgery, it is most likely ectasia.


